

Abonnez-vous aux SCP News
Cleaner production: What is it?

Cleaner Production allows:
- Savings to be made in raw materials, water and energy.
- The disposal, reduction and/or replacement of hazardous materials.
- The reduction in quantity and hazardousness of waste and emissions.
The reduction of impact during a product's life cycle, from the reception of raw materials to the final waste product.
The incorporation of environmental criteria in the design and distribution of services.
Cleaner production is a strategic tool of business policy, which integrates the environment in the global management of the company and enables it to maintain or improve competitiveness in a framework of sustainability of the environment. Its application requires responsible environmental management, a change of attitude and the evaluation and application of technological knowledge and options.
Cleaner production is an environmental management option which, in addition, has proved to be the stage prior to correct treatment or disposal alternatives, which with it is not incompatible.
This concept of integrated environmental prevention is known by several names of very similar meaning: minimisation, reduction at source, pollution prevention, cleaner production, ecoefficiency, etc.
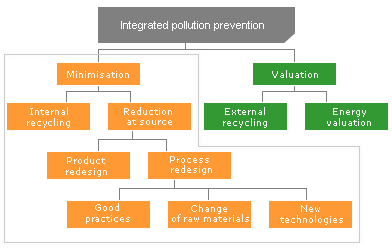
Advantages of Cleaner Production:
- Reduction of risk to the environment, health and of industrial accidents.
- Economic savings on raw materials, water and energy.
- Savings in waste flow management and treatment.
- Improvement of corporate image.
- Better quality of the product
- Fewer products which do not conform to specifications.
- Rationalisation of the work structure
- Improvement of routine habits and rethinking of processes and procedures.
- Optimisation of processes and resources
- Fulfilment of the company's environmental requirements and a commitment to its sustainable development.
Unlike end-of-pipe treatments, pollution prevention at source can be applied to the different stages of the productive process in most industrial processes.














